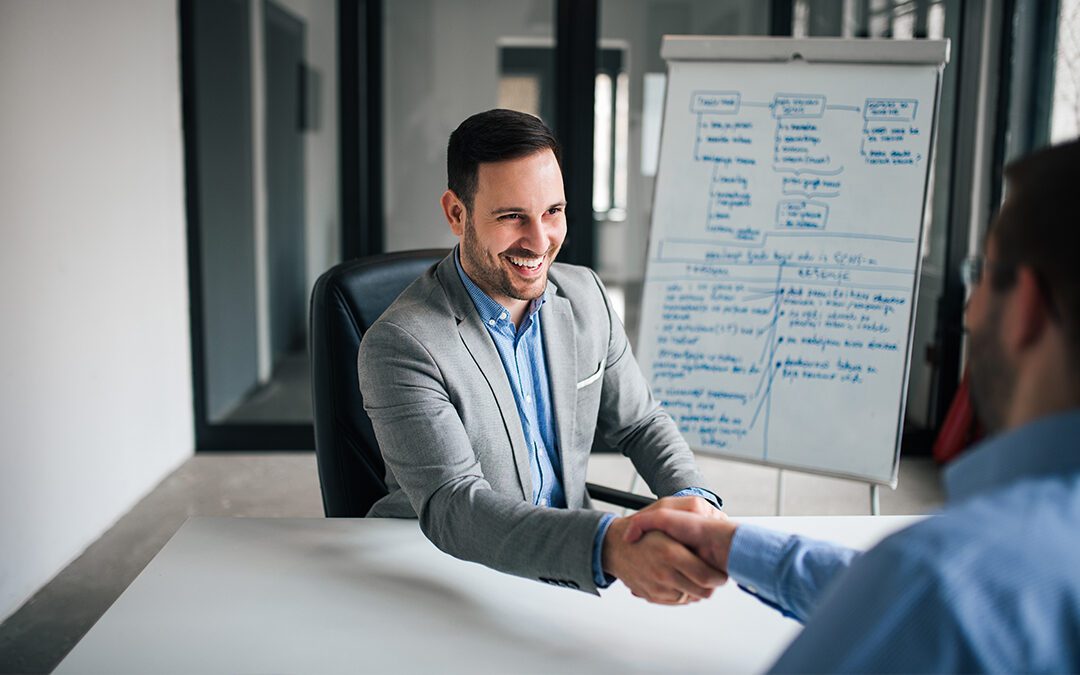
We all know that sales drive business growth. And that stronger sales individuals and teams can accelerate revenue growth. But great sales and business development individuals and teams don’t happen by accident. And it’s not simply a matter of hiring those with the best track record. Or those with the best sales skills.
To develop a sales team that performs well today and into the future requires collaboration among multiple stakeholders across the organization. It benefits from a clear competency model with a framework to define, measure, and develop the skills and competencies across and beyond the sales team. Here’s how a sales competency model can accelerate your business growth.
What is a sales competency model?
Training Industry defines a competency model as “a framework for defining the skill and knowledge requirements of a job. It is a collection of competencies that jointly define successful job performance.”
At Avilar, we talk about competencies as the skills, knowledge, and behaviors involved in how a person performs on the job:
- Skills are specific learned abilities. They are what a person can do. Writing a blog is a skill. So is computer programming, data entry, oral communication, and truck driving. Skills describe what activities individuals are trained to perform.
- Knowledge is information or an understanding of a principle gained through formal education or experience. It is what is known in a field; i.e. facts and information. Knowledge is what a person knows.
- Behaviors describe a person’s actions in response to a situation or another person. Behavior is what a person does.
A person can be competent at managing customer relationships, building teams, and facilitating meetings. They know what to do, how to do it, and they actually perform those actions over time.
A competency model defines the set of competencies as well as the proficiency level needed for each job. For example, while an individual contributor may need to be a proficient problem-solver, a team leader will need to be proficient at communication, problem-solving, organization, and delegation skills.
Quite simply, a sales competency model is a competency model that’s built specifically for sales teams.
How to build a sustainable sales competencies framework
HR may lead an effort to define skills and competencies across the company. However, as Josh Bersin has pointed out, “just developing skills does not make your company perform better. It’s how people use these skills that matters.”
For the company to get the desired “lift” from a skilled sales team, the skills and competencies that sales professionals develop should be intentional. They should be specific to the job roles in the company. And they should be aligned across the team and with the company goals to ensure that the skills and competencies that sales personnel develop are being used to achieve desired results.
That’s where the sales competencies framework comes in. When built correctly, sales competency models are tools that support a skills-first approach to hiring, performance management, training and development, and job promotions.
To succeed, your sales management must work closely with HR to build the skills and competency library, then “own” the framework that works for your sales team. Understanding that sales professionals and leaders grow in their jobs and careers as companies and markets grow around them, it’s important that your sales competencies framework stands the test of time.
There are sales competency models in the market, such as this ATD “World-Class Sales Competency Model,” created for companies “regardless of industry, geography, or size.” Whether you use a model from ATD or another source or build one of your own, you’ll want to customize the model to fit your organization.
When you’re ready:
- Define skills and competencies relevant to the sales team, aligned with company goals. Include soft skills and hard skills. Include perishable and durable skills.
- Map sales competencies to job descriptions. For inside and outside sales roles, sales operations, sales leadership, proposal writers, sales engineers, and all other sales-related jobs, identify required competencies AND the proficiency (beginner, fully functional, expert) required for each job and each level (junior, senior) of that job.
- Use sales competencies for the full employee lifecycle. From recruiting to onboarding, training and development, promotions, succession planning, and career development, your sales competency model should inform personnel plans, decisions, and actions.
- Refresh for emerging competencies. At least once a year, do a deep dive into the market to analyze the emerging skills and competencies. What are your competitors doing? What are prospective customers asking for? Be ready to add and remove competencies from your model as your business, the market, and technologies evolve.
Once the framework is established, skills assessments will validate the skills and competencies of your sales personnel. Continue to measure skills and competencies over time to measure progress and close skills gaps.
Ten essential competencies and skills of sales representatives
Over time, your competency model will provide the reference framework to guide the development of competencies and skills of sales representatives, informing training and development activities, and helping to benchmark individual progress toward proficiency goals.
Every sales team will have its own list of key skills for sales representatives. Here are just ten, inspired by a recent Hubspot article on top competencies identified by sales leaders:
- Foundational Sales Knowledge. An understanding of how sales works. Knowledge would include an understanding of a well-defined sales model used by the company to define progression through the stages of a sales pipeline.
- Communication Skills. To work in sales, excellent communication skills are a must. Writing emails and proposals are very different, but both are essential skills. Verbal communications – over the phone, in 1:1 conversations, and sales presentations to a group – are all important, too.
- Technology Skills. All team members should be adept at working with technology – from email to productivity tools to sales systems used to track and manage sales activities.
- Product or Service Knowledge. Sales staff must know what your company is selling and how it meets the needs of your customers better than those of your competitors in this market. They need to be able to conduct a simple product demonstration or provide examples of how offered services may help address a customer’s needs.
- Attention to Detail. Preparation and attention to detail show prospective customers that you respect them enough to learn what you can about their business before you meet and that you’ve done your research.
- Customer Service. Sales representatives understand how to serve customers and take pride in delivering great service.
- Solutions-Oriented. Sales personnel know how to position solutions to address real customer problems.
- Relationship-Building. Salespeople build a rapport with prospects and customers and follow through, over time, to strengthen that initial relationship.
- Negotiating Skills. Sales professionals provide customers with the products/services and features they need while ensuring your company is financially benefiting as well.
- Results-Driven. Effective salespeople are driven to get results. Their behaviors support guiding customers to take the next step toward a buying decision – or respectfully releasing a customer from the sales cycle, if the company offering is not a good customer fit at this time.
When developed and used correctly, sales competency models enable organizations to close skills gaps, guide career development, and generate bottom-line business results. Building and using the right sales competency model can support your organization’s strategy and growth.
Are you ready to build or refresh your sales competency model? Download our Competency Management Toolkit to see how a competency-first approach to sales can strengthen your organization. Or contact us to find out how our team and Avilar’s Competency Model or WebMentor Skills™ competency management system could help.
RELATED RESOURCES
Understanding Durable vs. Perishable Skills and How to Balance Them
Skills-Based Talent Management: What is it? Why is it Important?
Why You Should Boost Soft Skills in Your Organization
5 Important Questions to Answer Before Building a Competency Model